What is Cyber Security? The technique of protecting computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and…
The technique of protecting computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from hostile intrusions is known as cyber security. It’s also known as electronic information security or information technology security. The phrase is used in a range of contexts, ranging from business to mobile computing, and it may be broken down into a few categories.
Types of cyber threats
Types of cyber threats
Cybersecurity counters three types of threats:
- Cybercrime refers to individuals or groups who attack systems for monetary gain or to cause disruption.
- Cyber-attack are politically motivated data collecting attacks
- Cyberterrorism is intended to generate panic or dread by undermining electronic systems.
So if you are wondering, how do malicious actors gain access to computer systems? Here are some of the most typical ways that jeopardize the cyber-security:
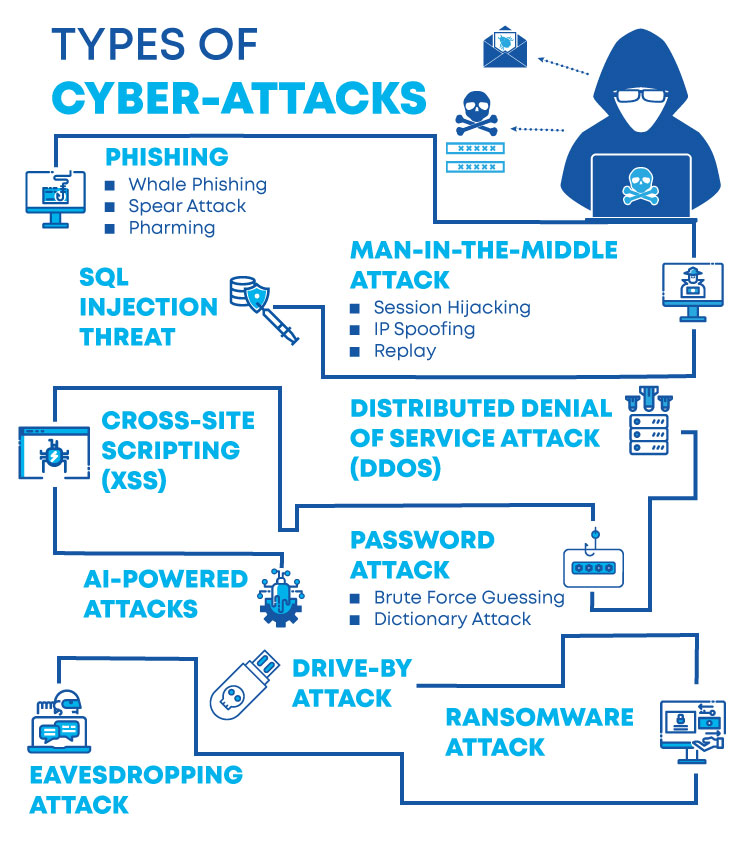
- Malware: Malware, sometimes known as “malicious software,” is an umbrella term for any malicious program or code that is destructive to computers. Malware is hostile, intrusive, and purposefully malicious software that aims to infiltrate, damage, or disable computers, computer systems, networks, tablets, and mobile devices by gaining partial control over their activities. Malware comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, including; Virus, Trojans, Spyware, Ransomware, Adware, Botnets
- SQL injection: SQL injection attacks, often known as SQLi attacks, are a type of vulnerability in website and web app code that allows attackers to take control of back-end operations and access, retrieve, and destroy sensitive data from databases.
- Phishing: Phishing is a type of social engineering in which an attacker sends a fraudulent message to a human target in the hopes of obtaining sensitive information or deploying harmful software on the victim’s infrastructure, such as ransomware.
- Man-in-the-middle attack (MITM): A man-in-the-middle attack is a type of cyber threat in which a hacker intercepts communication between two people to obtain information. On an insecure WiFi network, for example, an attacker could intercept data passing between the victim’s device and the network.
- Denial-of-service attack (DOS): A denial-of-service attack occurs when cybercriminals flood a computer system’s networks and servers with traffic, preventing it from fulfilling legitimate requests. This makes the system unworkable, prohibiting an organization from doing essential tasks.
Cyber safety tips – protect yourself against cyberattacks
How can organizations and individuals protect themselves from cyber-threats? Here are some of our best cyber-security recommendations:
- Keep your operating system and software up-to-date: As a result, you’ll get access to the most recent security fixes.
- Use strong passwords: Make sure your passwords are difficult to guess.
- Avoid clicking on email attachments from unknown senders: Email attachments from unknown senders should not be opened since they may contain virus.
- Do not click on links in emails or websites from unknown senders: This is a common method of malware distribution.
- Train employees in security principles: Establish basic security practices and regulations for employees, such as mandating secure passwords, and proper Internet use guidelines that spell out the consequences of breaching firm cybersecurity policy. Create guidelines for how to manage and protect customer information and other sensitive data.
- Protect information, computers, and networks from cyberattacks: Maintain a clean machine: the strongest defenses against viruses, malware, and other internet threats are the latest security software, web browser, and operating system. Configure your antivirus software to scan after each update. Other important software updates should be installed as soon as they become available.
- Protect your Internet connection with a firewall: A firewall is a collection of applications that work together to restrict unauthorized access to data on a private network. Make sure your operating system’s firewall is turned on, or download and install free firewall software from the internet. If your workers work from home, make sure their computers are protected by a firewall.
- Make a strategy for dealing with mobile devices: Mobile devices can pose serious security and management problems, especially if they contain sensitive data or have access to the business network. To prevent criminals from stealing information while the phone is on public networks, require users to password-protect their devices, encrypt their data, and install security software. Set up protocols for reporting missing or stolen equipment.
- Make backup copies of important business data and information: Back up your data on all PCs on a regular basis. Word processing papers, electronic spreadsheets, databases, financial files, human resources files, and accounts receivable/payable files are all examples of critical data. If possible, backup data automatically or at least regularly, and store the copies offsite or in the cloud.
- Control physical access to your computers and create user accounts for each employee: Unauthorized individuals should not be able to access or utilize commercial computers. Laptops are particularly vulnerable to theft or loss, so keep them locked up while not in use. Make sure that each employee has their own user account and require strong passwords. Only trusted IT staff and critical personnel should be given administrative privileges.
- Secure your Wi-Fi networks: If your office has a Wi-Fi network, make sure it is safe, encrypted, and hidden. Set up your wireless access point or router so that it does not broadcast the network name, also known as the Service Set Identifier, to hide your Wi-Fi network (SSID). The router’s access is password protected.
- Limit employee access to data and information and restrict software installation authority: Allowing a single employee access to all data systems is not a good idea. Employees should only have access to the data systems that they require for their tasks, and they should not be allowed to install software without permission.
- Passwords and authentication: Employees should be required to use unique passwords and change them every three months. Consider using multi-factor authentication, which requires more information than just a password to obtain access. Check with your sensitive data vendors, notably banking institutions, to discover if multi-factor authentication is available for your account.
Challenges of Cybersecurity
An organization’s cyber security activities must be coordinated across its whole information system in order to be effective. All of the following are considered cyber elements:
- Network security: The process of securing a network against unauthorized users, attacks, and intrusions.
- Application security: To guarantee that apps are secure from attacks, they must be updated and tested on a regular basis.
- Endpoint security: Remote access is a crucial aspect of doing business, but it can also be a data security vulnerability. The process of securing remote access to a company’s network is known as endpoint security.
- Identity management: In essence, this is a method of determining the level of access that each individual has within a company.
- Database and infrastructure security: Databases and physical equipment are at the heart of every network. It’s just as crucial to protect these devices.
- Cloud security: Many documents are stored in digital settings, also known as “the cloud.” Protecting data in an entirely online world poses numerous difficulties.
- Mobile security: In and of themselves, cell phones and tablets pose practically every form of security risk.
- Business continuity/disaster recovery planning: Data must be safeguarded and business must continue in the event of a breach, natural disaster, or other calamity. You’ll need a strategy for this.
- End-user training: Employees using the network or customers logging on to a firm app are examples of users. Good habits (password changes, 2-factor authentication, and so on) are a vital aspect of cybersecurity education.
Cybersecurity for Small Business
Government agencies and large corporations are commonly thought to be the most significant targets of hackers and cyberthreats. However, while these are extremely attractive goals, they are also extremely challenging.
Despite the fact that over 77 percent of all cyber-crimes target small and midsize enterprises (SMBs), data shows that 42 percent of SMBs do not consider cyber-crime as a threat. And in reality, hackers opportunists and are looking for valuable targets, but they’re also fine-tuning their tactics to go after low-hanging fruit. Small businesses combine the advantages of both environments. They have access to money and data, which makes them potentially profitable targets, but their defenses are typically far weaker.
It’s vital to protect your expanding company from cyber dangers, but it takes time and resources away from other growth efforts. When traditional security methods fail to resist modern assaults, the problem becomes even worse.
The Importance of Cybersecurity
Because government, military, business, financial, and medical organizations acquire, process, and store massive amounts of data on computers and other devices, cyber security is critical. Sensitive data, such as intellectual property, financial data, personal information, or other sorts of data, might make up a considerable amount of that data. Unauthorized access or exposure to that data can have serious implications.
Companies and organizations, particularly those responsible with preserving information linked to national security, health, or financial records, must take efforts to protect their sensitive business and people information as the volume and sophistication of cyberattacks grows.
Making the Investment
Accentuate has full range of enterprise cyber security services with best in class cyber security team and enterprise IT security experts, many of whom are Certified Security Professionals (CISSP, CEH) as well as certified IT product specialists. With vast experience in information assurance industry, Accentuate have been experimental in developing, evaluating and implementing cyber security policies, conducting risk assessments and performing related testing to secure and optimize our nation’s most critical and secret information technology systems.
Cybersecurity is a preventative strategy; you must invest in it before something bad happens to your company, not after it has already happened. As a result, the optimum moment to begin is right now. Whether or whether you “think” your small business is a frequent target of cybercriminals, the truth remains that all small businesses are at danger of being targeted. Accentuate can help you in formulating a strategy and help you to mitigate the risks of cyberattacks from cybercriminals by applying the latest and compliant methods. Even a small investment in cybersecurity defenses in 2021 and beyond should be enough to ward off and/or mitigate the majority of prospective threats.






